In this article we will discuss how to check the performance of a disk or storage array in Linux. IOPS (input/output operations per second) is the number of input-output operations a data storage system performs per second (it may be a single disk, a RAID array or a LUN in an external storage device). In general, IOPS refers to the number of blocks that can be read from or written to a media.
Most disk manufacturers specify nominal IOPS values, but in fact these are not guaranteed. To understand the performance of your storage subsystem prior to starting a project, it is worth getting the maximum IOPS values your storage can handle.
Using FIO (Flexible I/O) Tool for Storage Benchmarking
To measure disk IOPS performance in Linux, you can use the fio (the tool is available for CentOS/RHEL in EPEL repository). So, to install fio in RHEL or CentOS, use the yum (dnf) package manager:
# yum install epel-release -y
# yum install fio -y
Or apt-get in Debian or Ubuntu:
# apt-get install fio
Then you to identify the disks to test. The test is done by performing read/write operations in the directory your disk or LUN is mounted to.
Let’s do several types of disk IOPS performance tests in various disk load scenarios (a test mode you select depending on a hosted app logic and general infrastructure of a project).
Random Read/Write Operation Test
When running the test, an 8 GB file will be created. Then fio will read/write a 4KB block (a standard block size) with the 75/25% by the number of reads and writes operations and measure the performance. The command is as follows:
# fio --randrepeat=1 --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --gtod_reduce=1 --name=fiotest --filename=testfio --bs=4k --iodepth=64 --size=8G --readwrite=randrw --rwmixread=75
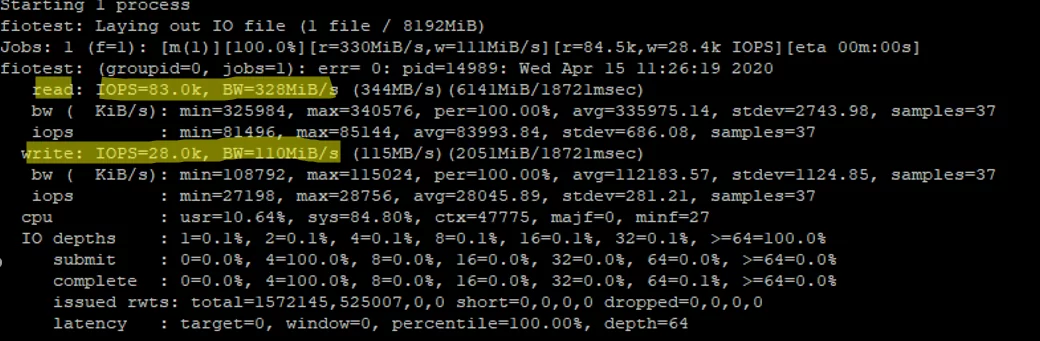
I ran my first test on an array that consisted of two SSDs and got good results:
- Read: 3280MiB/s, IOPS avg 83000
- Write: 110MiB/s, IOPS avg 28000
Since we have run a combined read/write test, the values for the separate tests will be higher.
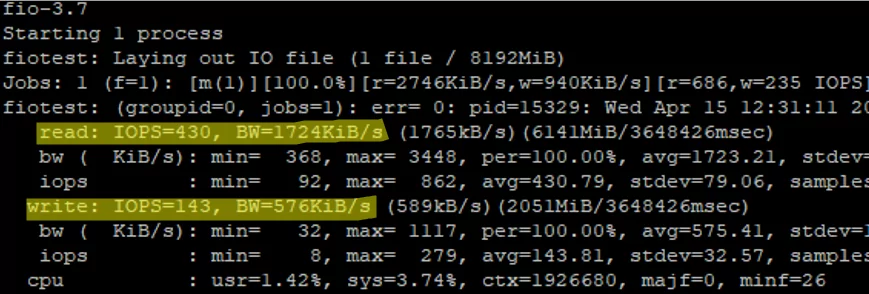
In comparison, I measured the performance on a SATA drive:
- Read: IOPS=430, BW=1.7 MiB/s
- Write: IOPS=143, BW= 0.6 MiB/s
Of course, the HDD results are worse than those of the SSD.
Random Read Operation Test
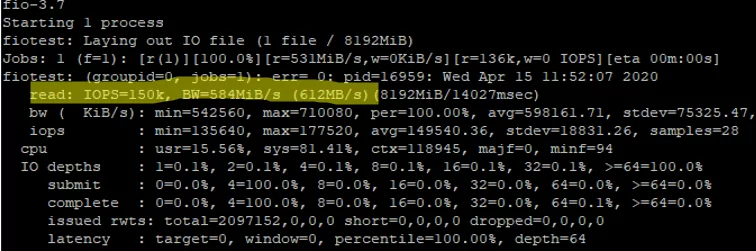
To measure disk performance for random read operations only, run the following command:
# fio --randrepeat=1 --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --gtod_reduce=1 --name=fiotest --filename=testfio --bs=4k --iodepth=64 --size=8G --readwrite=randread
The final part of the command was changed to —readwrite=randread.
As I told earlier, the read/write performance will be higher if measured separately:
READ: IOPS=150k, BW=584MiB/s (612MB/s)
Random Write Operation Test
To measure disk performance for random write operations, run this command:
# fio --randrepeat=1 --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --gtod_reduce=1 --name=fiotest --filename=fiotest --bs=4k --iodepth=64 --size=8G --readwrite=randwrite
So you can perform a storage load test on your server prior to launching a project and check the highest performance values. However, the test doesn’t guarantee that your disk array or disk will show the same performance constantly, but it is worth to take the test on the initial stage of a project. Learn how to test IOPS in Windows in this article.